Watch
Review the interview with script producer Jessica Paine to explore the morality question, is Artificial Intelligence (AI) good or bad?
Activity
Cat realises that the culprit behind the phone hack wasn’t a person, but AI: Hermes Artificial Neurotech Collection (HANC). HANC is the source of the data leak, using a large language model to communicate with the spoken word.
What is HANC able to do?
Document the capabilities of HANC to define what type of AI this technology is.
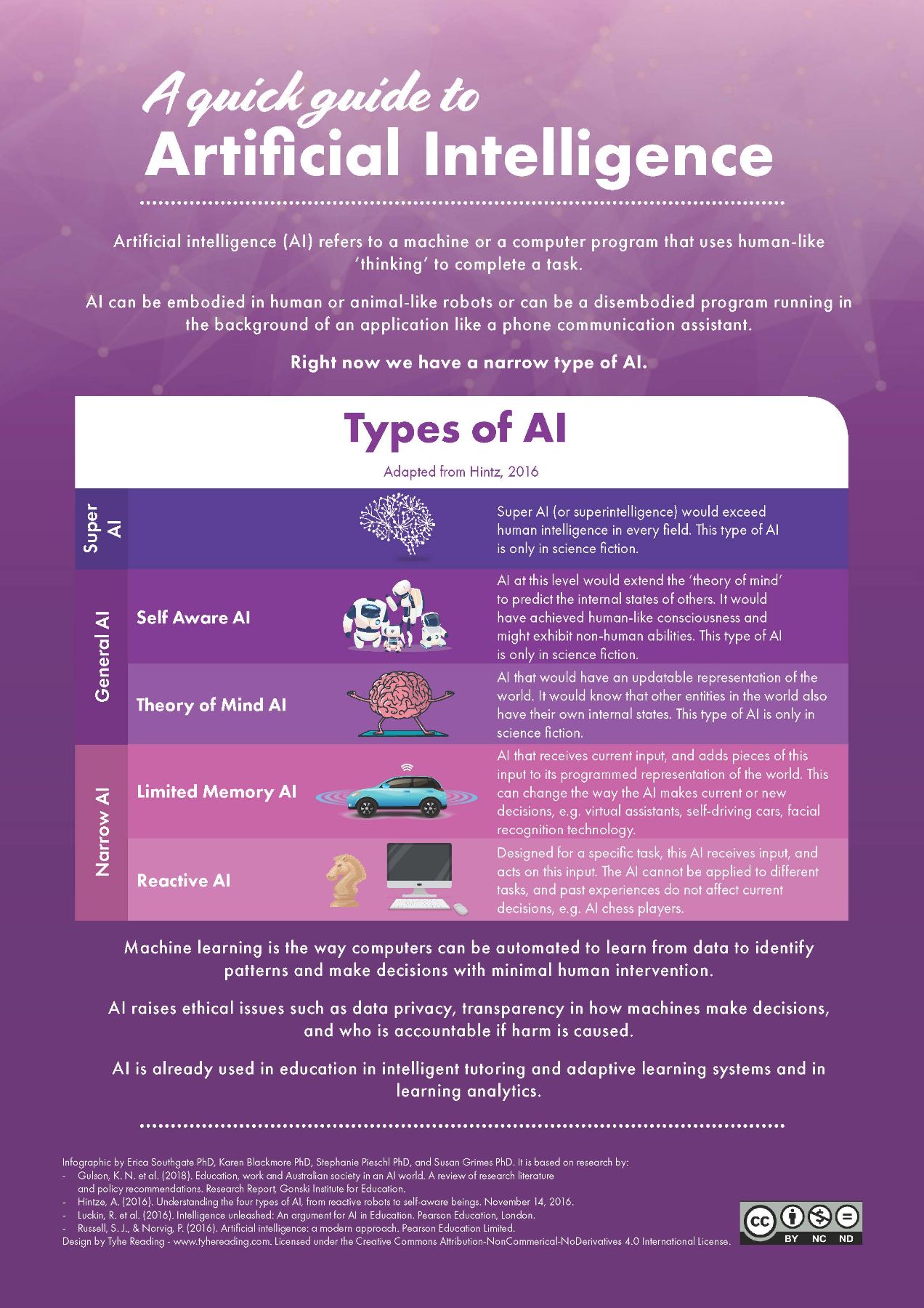
Then, reference the infographic below to categorise what type of AI HANC is.
Note
AI in The PM’s Daughter is speculative (Science Fiction), which goes beyond capabilities in the current day. Experts place our current development stage in the ‘Narrow AI’ band.
A quick guide to AI. Infographic by Erica Southgate PhD, Karen Blackmore PhD, Stephanie Pieschl PhD, and Susan Grimes PhD.